Google Search Console (GSC) has become an essential tool for website owners, digital marketers, and SEO professionals in 2025. It offers invaluable insights into how Google crawls and indexes your website, helping you monitor your site’s performance, identify issues, and optimize for better search rankings. By using GSC, you can track vital metrics such as search impressions, click-through rates (CTR), keyword rankings, and more.
In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through the process of leveraging Google Search Console to scale your website traffic effectively. Whether you’re looking to fine-tune your content, improve your search visibility, or enhance your site’s overall performance, GSC is the key to unlocking actionable insights that can drive measurable growth.
What is Google Search Console?
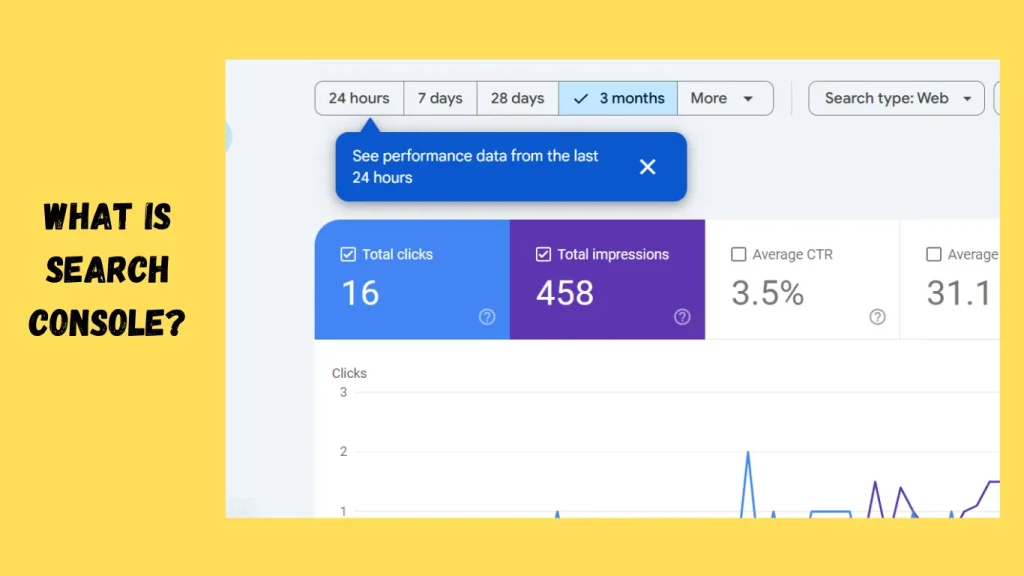
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool provided by Google that helps website owners and webmasters monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot their site’s presence in Google Search results. It provides direct insights from Google about how your website is being crawled, indexed, and displayed in search results, making it an essential resource for SEO optimization.
Why GSC is Essential for SEO:
- Performance Insights: GSC allows you to track important performance metrics like impressions, clicks, click-through rates (CTR), and average search positions for specific queries. These insights help you identify which keywords are driving traffic to your site and where you can improve for better results.
- Crawl and Indexing Reports: GSC provides detailed information about how Googlebot crawls your website. You can view crawl errors, pages that were not indexed, and any issues preventing proper indexing, which is crucial for maintaining your site’s visibility in search.
- Mobile Usability and Core Web Vitals: In today’s mobile-first world, GSC allows you to monitor mobile usability and optimize your website for better user experience. It also provides insights on Core Web Vitals, which impact rankings based on site performance, such as page load times, interactivity, and visual stability.
- Fixing Technical Issues: Google Search Console helps you identify technical issues like broken links, sitemap errors, or security concerns that might hinder your site’s SEO performance. The sooner you address these issues, the better your chances of ranking well on Google.
- Search Appearance and Rich Results: GSC lets you see how your site appears in search results, including rich snippets and structured data. Optimizing these elements can enhance visibility and engagement with your content.
Direct Google Data vs Third-Party Tools:
While there are many third-party SEO tools available, such as SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz, Google Search Console offers a significant advantage by providing direct data from Google itself. This data is more accurate and trustworthy because it reflects the real behavior of Googlebot and the performance of your website in Google’s index.
- Accuracy: GSC shows you data directly from Google’s perspective, which eliminates any discrepancies that might arise when using third-party tools that rely on web crawlers or estimated data.
- Real-Time Data: GSC offers near real-time insights into your website’s performance, allowing you to monitor fluctuations in impressions, clicks, and rankings as they happen.
- No Data Gaps: Unlike third-party tools that might not have full access to your site’s data (especially for private or non-public pages), GSC gives you comprehensive visibility into all aspects of your website’s search performance.
- Free Access: Google Search Console is completely free, unlike many third-party SEO tools that often require subscriptions or payments to access advanced features. This makes it an invaluable resource for anyone looking to improve their SEO without breaking the bank.
By utilizing GSC, you’re working with the most reliable and direct data source available, making it an indispensable tool for SEO success.
Understanding Google Search Console Reports

Google Search Console provides a variety of reports to help you understand how your website is performing in search results. One of the most important reports is the Performance Report, which provides critical insights into your site’s visibility, traffic, and how it ranks for various queries. The main metrics you’ll find in the performance report include Clicks, Impressions, Click-Through Rate (CTR), and Position.
Introduction to the Performance Report Metrics
- Clicks:
This metric shows the number of times users clicked on your website’s link after seeing it in Google search results. It’s a clear indicator of how well your site is attracting traffic from search engines. A higher number of clicks suggests that your website is providing relevant content that users are interested in. - Impressions:
Impressions reflect how often your website’s URL was displayed in Google search results for a particular query, regardless of whether the user clicked on it. An impression is counted whenever your site appears in search results for any query, even if the user doesn’t interact with it. Impressions give you an understanding of your site’s visibility and reach in the search engine results page (SERP). - Click-Through Rate (CTR):
CTR is the ratio of clicks to impressions, expressed as a percentage. It tells you how effective your listings are at encouraging users to click. A high CTR means that the title, meta description, and other elements of your page are compelling users to engage with your content. Conversely, a low CTR might indicate that your meta tags are not enticing enough, and you may need to improve them.
CTR Formula:
CTR=(ClicksImpressions)×100\text{CTR} = \left( \frac{\text{Clicks}}{\text{Impressions}} \right) \times 100CTR=(ImpressionsClicks)×100 - Position:
This metric represents the average position of your website’s URL for a specific search query. A lower number (e.g., position 1 or 2) means that your site is ranking high on Google’s search engine results page (SERP), while a higher number (e.g., position 20) indicates a lower ranking. Position is vital for understanding how competitive your keywords are and where your website stands relative to others.
Deep Dive into Impressions and Their Importance
Impressions are often an overlooked but crucial metric when assessing SEO performance. Although they don’t directly reflect user engagement, impressions provide valuable insight into your website’s visibility and reach.
Visibility in Search Results
Impressions show how frequently your pages are appearing in search results. Even if users are not clicking on your link, this data reflects the potential exposure your website is receiving. If your impressions are high but your clicks are low, it suggests that your content is visible but not compelling enough for users to click. This could point to issues with your meta titles or descriptions, or it could mean your content needs to be more relevant to the search intent.
Tracking Keyword Performance
Impressions help you track how often your site shows up for specific search queries. This allows you to monitor performance across different keywords. For instance, if you’re targeting a highly competitive keyword, you might see high impressions but lower CTR and ranking. Over time, as you optimize your content and improve its relevance, you should see both impressions and clicks increase for those targeted keywords.
Identifying New Opportunities
Impressions can uncover new opportunities. If a page is generating impressions for a query you weren’t targeting directly, this is an opportunity to further optimize that page for that keyword. By adding more relevant content, keywords, or addressing the search intent, you can boost both impressions and clicks for those terms.
Long-Tail Keywords:
Impressions give insight into how often your website is shown for long-tail keywords, which typically have lower search volume but can result in high-conversion traffic. High impressions with a low CTR can signal that your site is ranking for many niche or long-tail queries, and you may just need to optimize content for better CTR or position.
A/B Testing and Iteration
By looking at how impressions correlate with changes to your site (such as a redesigned page or updated meta description), you can track the impact of your SEO efforts. If you notice that impressions increase after an update but clicks do not follow, it indicates that you may need to adjust your copy or improve other aspects of your page to encourage engagement.
Tracking Seasonality and Trends
Impressions can also highlight seasonality and changing trends in search. For example, during holidays or specific events, you may see a spike in impressions for certain queries. By monitoring these trends, you can better time your content updates and promotions to align with increased search activity.
Using Google Search Console for Keyword Research

Google Search Console (GSC) can be an incredibly powerful tool for keyword research, helping you uncover high-traffic keywords and ranking opportunities. By leveraging GSC’s performance reports, you can make informed decisions about optimizing your content for organic growth.
Here’s how you can use GSC for keyword research:
How to Identify High-Traffic Keywords and Ranking Opportunities
- Accessing the Performance Report:
- Open GSC and navigate to the Performance section under the Search Results tab.
- This report displays data on clicks, impressions, CTR (click-through rate), and average position for all queries that lead to your site.
- Filter by date to analyze current keyword performance or compare to historical data.
- Sort by Clicks or Impressions:
- Clicks: Sorting by the number of clicks helps you identify the keywords that are already bringing traffic to your site. However, if you want to discover new opportunities, focus on Impressions first.
- Impressions: A high number of impressions means your content is appearing frequently in search results for a specific query, but it may not be getting enough clicks. If the CTR is low, this indicates a ranking opportunity where you can improve your content or meta tags to increase engagement.
- Analyze CTR and Position:
- CTR: If certain keywords have a high number of impressions but low CTR, this suggests that your pages are ranking for relevant keywords but need more compelling titles or meta descriptions to encourage clicks. Optimizing these can lead to significant improvements in traffic.
- Position: By looking at the Position metric, you can discover keywords that your site ranks for, even if they are not on the first page of search results. Keywords that rank in the top 10 but have room to improve (e.g., position 8 or 9) are prime candidates for optimization.
- Use Filter for Specific Queries or Pages:
- To narrow down your keyword research, use the Filter options in the Performance report to focus on specific queries or individual pages. This allows you to zoom in on keywords that are relevant to your content and audience, or to identify high-performing pages that may have further ranking opportunities.
Using Keyword Data to Boost Organic Reach

Target Keywords with High Impressions and Low CTR:
If you notice that certain keywords have high impressions but low CTR, focus on improving your page titles, meta descriptions, and content. These elements play a major role in convincing users to click on your link.
Try testing different variations of your meta tags and headlines, and see which ones drive more clicks.
Optimize for Long-Tail Keywords:
Long-tail keywords (more specific and less competitive) often generate lower impressions but higher conversion rates. Look for long-tail keywords with decent impressions and CTR. These keywords can be easier to rank for and are more likely to drive highly targeted traffic.
Once you identify these keywords, create content specifically targeting them. For example, if you’re ranking for a broad term like “travel tips,” you may notice long-tail queries such as “budget travel tips for solo travelers” or “travel tips for first-time visitors to Japan.” These can be opportunities to create focused blog posts.
Content Gap Analysis:
Look for keywords that your competitors might be ranking for but that you are not yet targeting. You can use the Comparison Tool in GSC to compare performance across different pages or queries. If you find a keyword with decent impressions but poor performance on your site, consider revisiting your content strategy for that keyword.
For example, if your competitor is ranking well for “affordable travel destinations for families” and you’re only ranking for “affordable travel destinations,” there is a content gap that you can fill by creating more specific content that addresses family-oriented travel tips.
Create More Relevant Content:
If you see keywords that are consistently bringing traffic (clicks and impressions) but have the potential to perform better, you can build additional content around those topics. You could create landing pages, blog posts, FAQs, or videos that target these keywords and enhance user experience.
For instance, if a page ranks for “vegan travel destinations” but you notice keywords like “best vegan food in Bali” are generating impressions, consider adding or expanding content on specific vegan-friendly activities or restaurants in Bali.
Improve Your Content’s Relevance to Search Intent:
Using GSC data, you can analyze how your content matches user intent. If your impressions are high but CTR is low, it may indicate that the user intent behind those queries doesn’t align well with the content on your site.
Revise the content to ensure it answers the query better and is more relevant to the searcher’s intent. For example, if users are searching for “quick vegan meals for dinner” and your page focuses more on general vegan recipes, you could refine your content to address fast meal prep for busy users.
Monitor Keyword Trends Over Time:
Keep an eye on your high-ranking keywords and their performance trends over time. This will help you spot any upward or downward movement in impressions, clicks, and CTR. If you notice a drop in performance for certain queries, it’s a good idea to investigate why this happened (e.g., changes in search algorithms, new competitors, etc.), and you can adjust your content accordingly.
In Conclusion, Google Search Console is a valuable tool for keyword research and optimizing your site’s organic reach. By analyzing impressions, clicks, CTR, and position data, you can identify high-traffic keywords and new ranking opportunities. Armed with this keyword data, you can focus on creating content that meets user intent, optimize existing pages for better CTR, and continually refine your SEO strategy for sustained growth.
Optimizing Pages with Google Search Console Data
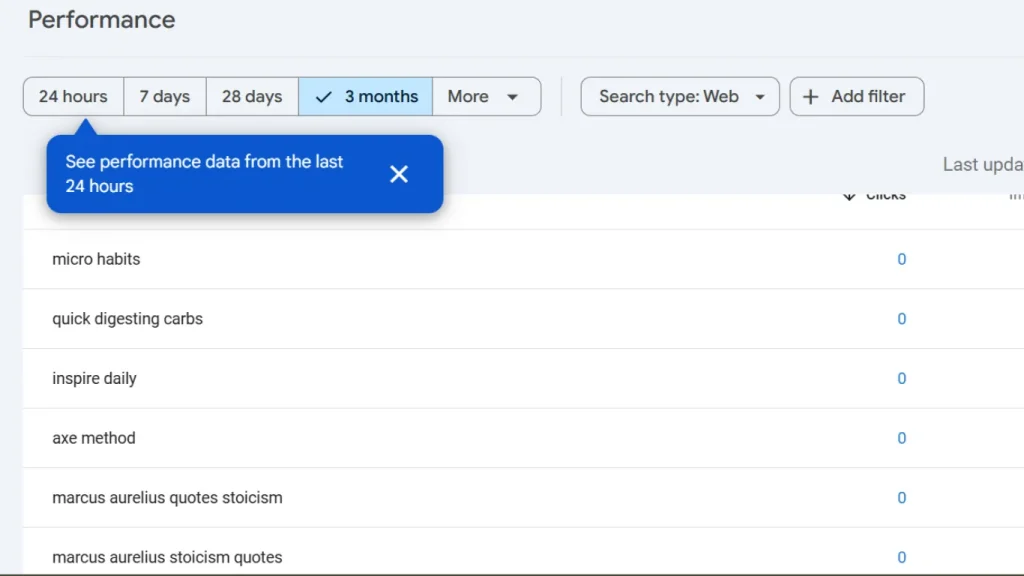
Google Search Console (GSC) provides actionable insights to improve your on-page SEO and enhance search rankings. By incorporating relevant keywords identified in GSC into your content, meta tags, and internal linking, you can significantly improve your site’s performance.
Here’s how you can optimize your pages using GSC data:
How to Optimize On-Page SEO Using GSC Data
Identify Underperforming Keywords:
From GSC’s Performance report, focus on keywords that have high impressions but low clicks (low CTR). These are the keywords where your page has the potential to rank better with just a little optimization.
For example, if you notice the query “healthy breakfast recipes” has high impressions but low CTR, it indicates that you’re appearing for the keyword but not attracting enough clicks. This could be because the content isn’t compelling enough or the meta tags aren’t optimized.
Update Page Titles and Meta Descriptions:
Titles and meta descriptions play a crucial role in CTR. If you see keywords with good impressions but low CTR, adjusting the page’s title and meta description can encourage more clicks.
Example: If your page is ranking for the query “best budget travel tips,” but the title is generic (e.g., “Travel Tips”), updating it to something more targeted and clickable like “Top 10 Budget Travel Tips for 2025” may improve your CTR.
Make sure the keyword appears naturally in both the title and meta description. This will help search engines understand the relevance of your content for those keywords.
Incorporate High-Traffic Keywords into Content:
If you notice specific keywords that bring in traffic but have the potential to rank higher, try naturally incorporating them into your content.
Use them in headings (H1, H2, H3), throughout the body text, and in image alt text. Ensure the keyword placement feels natural and maintains content quality.
Example: If you’re ranking for “best vegan recipes for dinner,” add more variations of this keyword into the body of the content like “easy vegan dinner ideas” or “quick vegan meal options” in a way that improves the article’s comprehensiveness.
Use Internal Linking:
Internal linking helps search engines understand the structure of your website and boosts page authority for specific keywords. When you identify a keyword that’s ranking well or has the potential to rank higher, link to that page from other relevant pages on your site.
For example, if you have a page on “easy vegan recipes” and you’re targeting the keyword “vegan meal prep,” link internally from a blog post on meal prep to the page that targets the “vegan meal prep” keyword.
Optimize for User Intent:
GSC helps you understand search intent behind specific keywords. If your impressions are high but CTR is low, it could indicate that the content isn’t addressing the user’s needs fully. Use this data to match your content with what searchers are looking for.
Example: If your content is ranking for “vegan recipes for beginners” but isn’t converting well, you might need to focus more on step-by-step instructions, beginner-friendly tips, or shorter recipe times to match the search intent.
Add Structured Data (Schema Markup):
Adding structured data (schema markup) can improve the visibility of your pages in search results and can help your pages stand out with rich snippets. If you’re ranking for queries like “best vegan breakfast recipes,” using structured data for recipes can enhance the page’s listing in SERPs with additional details like cooking time, ingredients, and ratings.
Use GSC’s Rich Results Report to check if your pages are eligible for rich snippets and what improvements are needed.
Improve Mobile Friendliness:
A key ranking factor in Google’s algorithm is mobile-friendliness. If you’re seeing impressions for mobile queries but low performance, check the Mobile Usability section in GSC to identify any issues with your site’s mobile version.
Example: If a page ranks well for “affordable online courses” but mobile users are bouncing, ensure that your mobile version is fast and easy to navigate.
Examples of Small Changes that Can Improve Search Rankings
Title Tag Optimization:
Before: “SEO Tips for 2025”
After: “Top 10 SEO Tips to Boost Your Rankings in 2025”
Why: This change adds specificity and urgency, encouraging more clicks.
Meta Description Update:
Before: “Learn SEO strategies to improve rankings.”
After: “Discover 10 proven SEO strategies for boosting your website’s rankings in 2025. Start optimizing today!”
Why: The new description is more compelling, includes a call-to-action, and incorporates a relevant keyword (“boosting rankings”).
Adding Keywords to Subheadings:
Before: The content is titled “Top Vegan Recipes,” but there are no subheadings targeting specific long-tail keywords.
After: Add subheadings like “Easy Vegan Breakfast Ideas” or “Quick Vegan Dinner Recipes.”
Why: These subheadings target more specific queries and help break up the content, improving readability and SEO.
Optimizing for Featured Snippets:
Before: The page discusses general SEO tips but doesn’t use clear formatting.
After: Include an easy-to-read listicle or table format with bulleted points for each SEO tip. Markup with schema data if possible.
Why: Google tends to feature list-based or “how-to” content in featured snippets. Clear formatting can help increase the chance of being featured.
Internal Linking for Relevant Keywords:
Before: No internal links pointing to your page on “beginner yoga routines.”
After: Add a link from a related blog post on “fitness for beginners” to your yoga page.
Why: This increases the page’s authority for the target keyword and helps search engines discover it more easily.
Improving Content for Voice Search:
Before: The page is optimized for traditional search queries.
After: Rework some content to be more conversational and question-based (e.g., “What are the best vegan dinner ideas for beginners?”).
Why: Voice search queries are often phrased as questions, and optimizing content for these can help increase visibility in voice search results.
By using the data provided by Google Search Console, you can make informed and effective optimizations to improve your pages’ SEO performance. Even small adjustments—like tweaking titles, improving CTR, or adding internal links—can make a significant difference in your search rankings. GSC gives you the insights you need to target the right keywords, improve content relevance, and ultimately drive more organic traffic to your site.
Technical SEO with Google Search Console

Technical SEO ensures that search engines can crawl, index, and understand your website’s content. Google Search Console (GSC) is a vital tool in identifying and fixing technical SEO issues that could impact your website’s visibility. In this section, we’ll explore how to identify common technical issues, use the URL Inspection Tool, and leverage regular expressions for troubleshooting.
1. Identifying Common Technical Issues with GSC
Google Search Console helps you identify a variety of technical issues that could hinder your website’s SEO performance. Common issues include:
404 Errors (Page Not Found)
A 404 error occurs when a page on your website is not found or has been deleted, but search engines or users still attempt to access it.
- How to track: In GSC, navigate to Coverage under the Index section. Here, you will see if Googlebot has encountered any 404 errors when crawling your site. Pages with the status “Not Found” or “404” are listed here.
- How to fix: Once identified, you can either:
- Redirect the URL to an appropriate live page using a 301 redirect.
- Fix broken links if they point to pages that no longer exist.
- Remove the page from the sitemap if it no longer serves a purpose.
Soft 404s
A soft 404 happens when a page returns a “200 OK” status code but still displays a “Page Not Found” message, confusing search engines.
- How to track: In the Coverage report, you may notice some URLs flagged as Soft 404.
- How to fix: Ensure that pages that are no longer relevant return the correct 404 or 410 status. Alternatively, create meaningful content or redirects to ensure that users and Google can access useful pages.
Redirect Chains
Redirect chains occur when a URL redirects to another URL, which then redirects to a third, and so on. Multiple redirects slow down page load times and can impact SEO.
- How to track: Google Search Console provides information in the Crawl Errors section and URL Inspection Tool, but you might need third-party tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs for a full view of redirect chains.
- How to fix: Avoid unnecessary redirects by ensuring URLs only have one redirect path. For example, if URL-A redirects to URL-B and then URL-B redirects to URL-C, ensure URL-A directly points to URL-C.
Mobile Usability Issues
Given Google’s mobile-first indexing, mobile usability issues can affect your rankings. These include problems such as clickable elements being too close together or text being too small.
- How to track: In Mobile Usability, Google Search Console highlights any issues that affect mobile users.
- How to fix: Ensure your website is responsive and the text is readable on all devices. Consider adjusting font sizes, making links and buttons larger, and improving mobile layout.
2. Using the URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection Tool in GSC allows you to check how Googlebot sees a specific URL on your website. This tool can help troubleshoot technical issues such as indexing problems or crawling errors. Here’s how you can use it effectively:
How to Use the URL Inspection Tool
- Inspect a URL: Enter any URL from your site into the Search bar of the URL Inspection Tool. Google will retrieve data related to that URL.
- View the results:
- Indexing status: See whether the page is indexed or excluded.
- Crawl status: View the last crawl date and whether there were any crawl issues.
- Mobile Usability: Check if the page passes mobile-friendly tests.
- Core Web Vitals: Assess the page’s load times and overall user experience on mobile.
What to Do with the Data
- If the page isn’t indexed, use the tool to request indexing.
- If the page has technical issues like blocked resources (e.g., CSS or JavaScript), you’ll see the status in the inspection tool, allowing you to resolve them.
- If Google cannot access the page, ensure your robots.txt file or meta tags are not blocking the page.
3. Using Regular Expressions for Troubleshooting
Regular expressions (regex) are powerful tools for pattern matching, which can help filter large amounts of data and identify specific issues in GSC. Here’s how you can use regex for technical troubleshooting:
Filtering and Finding Specific URLs or Issues
- Regex for URL patterns: In GSC, you can filter data using regex in reports like Coverage or Performance to find URLs matching a specific pattern.
- Example: Use ^https:\/\/www\.yourdomain\.com\/.*\/ to find all URLs on your domain that contain a certain path or structure.
- Regex for identifying common errors: You can use regex to find pages that might have 404 errors or soft 404s by searching for URL patterns that are broken.
- Example: Use 404 to filter out pages that may return a 404 status or similar errors in the URL Inspection or Coverage reports.
Benefits of Using Regex in GSC
- It helps in spotting trends across your site.
- It allows you to narrow down specific issues, like finding all URLs that return a certain status code.
- It can aid in identifying duplicate content issues or pages that need restructuring.
4. Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
SEO and technical maintenance should be ongoing. Regularly monitor your GSC account for new issues, and fix them as they arise. Key areas to track regularly include:
- Index Coverage: Ensure all important pages are indexed and not excluded.
- Crawl Stats: Check for any crawl anomalies that could prevent Google from accessing key pages.
- Core Web Vitals: Ensure that performance metrics are kept within optimal ranges to avoid ranking penalties.
Advanced Tips for GSC Users
Google Search Console (GSC) provides a wealth of data, but to truly harness its power and gain deeper insights, you need to go beyond the basic reports. By exporting data to spreadsheets, using filters, and leveraging regular expressions (regex), you can dive into more advanced SEO analysis and make more data-driven decisions.
1. Exporting GSC Data to Spreadsheets for Deeper Analysis
One of the best ways to analyze large amounts of data in Google Search Console is by exporting it into a spreadsheet. This allows you to manipulate and visualize the data further, offering insights that may not be as easily visible in GSC’s interface.
How to Export Data from GSC
- Navigate to the relevant report:
- Open GSC and go to the Performance, Coverage, or Mobile Usability reports (or whichever report you’re interested in).
- Select the date range:
- GSC allows you to customize the time period for your data. Choose a specific date range or compare periods (e.g., last 7 days, last 28 days).
- Click on the “Export” button:
- In the top-right corner of the report, there’s an Export button. Click it to download your data.
- You can export in either CSV or Google Sheets formats, depending on your preference.
- Customize the export (if needed):
- For example, in the Performance report, you can choose to export data by clicks, impressions, CTR, and position, or apply filters such as queries, pages, countries, or devices.
Why Export Data?
- Advanced Filtering and Sorting: Spreadsheets allow for more advanced filtering and sorting than GSC itself, helping you uncover patterns in your data.
- Visualization: Once in a spreadsheet, you can create charts and graphs to visualize trends, such as which keywords are driving the most traffic over time.
- In-depth Analysis: Analyzing the data in a spreadsheet lets you calculate metrics or set up pivot tables, allowing you to compare different segments of your website or data set side by side.
Example Use Cases for Exported Data:
- Tracking keyword performance over time to identify rising or falling keywords.
- Analyzing CTR for pages with similar impressions to determine which content performs best.
- Identifying keyword cannibalization by checking if multiple pages are ranking for similar keywords.
2. Using Filters and Regular Expressions for Advanced Insights
Google Search Console has powerful filtering tools, but to get even more granular insights, you can apply filters and use regular expressions (regex). This can help you quickly identify problems, trends, or opportunities that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Using Filters for Advanced Segmentation
Filters in GSC allow you to narrow down data based on specific criteria, making it easier to focus on key areas of interest.
Common Filters to Use:
- Query Filter: Focus on specific keywords. For example, filter for high-performing keywords or keywords that have the potential to bring in more traffic.
- Page Filter: Focus on individual pages on your site. If a specific page is underperforming, use this filter to analyze it separately.
- Device Filter: Check performance on different devices (mobile, desktop, tablet) to identify where issues might exist.
- Country Filter: Analyze performance in specific geographic locations.
How to Apply Filters:
- Navigate to the Performance report or any other report where filtering is available.
- Click the filter icon next to the metric you want to filter by (e.g., queries, pages, devices).
- Choose from the available options or input custom filters.
Filters let you break down your data to specific segments, allowing for a much deeper and actionable analysis.
Using Regular Expressions (Regex) for Advanced Filtering
Regular expressions are a powerful way to create more complex and customized filters, especially when dealing with large datasets. Regex allows you to match patterns within your data, enabling you to uncover insights that can’t be easily discovered through basic filters.
Regex Use Cases in GSC:
- Finding specific URL patterns: For example, you can use regex to filter all URLs that contain a certain word or structure (like category/ or product/).
Example: ^https:\/\/www\.yourdomain\.com\/category\/.* will match all URLs under the /category/ path. - Identifying specific query patterns: Regex can help identify keywords with certain patterns, like those that contain a particular phrase or match certain lengths.
Example: ^.*(buy|purchase).* will match all queries that contain the words “buy” or “purchase.” - Excluding unwanted data: Regex can help you exclude specific queries or pages that you do not want to analyze, such as those related to your site’s terms and conditions or privacy policy.
Example: ^((?!terms|privacy).)*$ excludes queries or pages with “terms” or “privacy” in the URL or query.
How to Use Regex in GSC:
- Go to the report you want to filter (e.g., Performance).
- Click on the “Filter” option, and then select Custom to apply a regular expression.
- Enter your regex pattern into the filter box. Make sure it’s formatted correctly, as even small mistakes can result in inaccurate filtering.
Benefits of Regex in GSC:
- Custom Precision: Regex gives you the ability to create highly specific filters that standard filters cannot.
- Identifying Patterns: You can spot keyword trends or issues that span across multiple pages or queries, giving you more actionable insights.
- Complex Exclusions: You can exclude specific subsets of your data based on patterns, such as excluding branded keywords, specific pages, or low-performing queries.
3. Regular Monitoring and Iteration
Once you’ve mastered exporting and filtering data using regex, it’s important to monitor changes over time. Regularly check your Performance report, Coverage data, and other relevant sections of GSC to ensure that your website is performing optimally. By continuously analyzing and iterating on your SEO strategy based on GSC data, you can keep improving your website’s search visibility.
Common Troubleshooting Tips for Google Search Console

Google Search Console (GSC) is a powerful tool for monitoring the health and performance of your website in Google Search. However, like any SEO tool, it may sometimes show errors or issues that need addressing. Troubleshooting these issues is essential to ensure your site is properly indexed and accessible to search engines.
Below are common problems you may encounter and actionable tips for resolving them, particularly focusing on indexing issues.
1. Addressing Indexing Problems
Indexing issues are one of the most common reasons your pages might not appear in search results, or they might appear with poor rankings. GSC offers a range of reports that can help you identify whether your pages are being indexed properly.
Steps to Identify Indexing Problems:
- URL Inspection Tool:
- Use the URL Inspection Tool to check if specific pages are indexed. Enter the URL into the tool and check the status. If the page is not indexed, GSC will often provide insights into why.
- Coverage Report:
- In the Coverage section, GSC shows pages with different indexing statuses: “Error”, “Valid with warnings”, “Valid”, and “Excluded”. These categories help you pinpoint the exact problem with indexing.
- Errors: This indicates pages that cannot be indexed due to technical issues.
- Valid with warnings: Pages are indexed, but there are minor issues that may affect performance.
- Excluded: Pages that Google has chosen not to index, and you may need to investigate further.
- In the Coverage section, GSC shows pages with different indexing statuses: “Error”, “Valid with warnings”, “Valid”, and “Excluded”. These categories help you pinpoint the exact problem with indexing.
Common Indexing Problems and How to Fix Them:
- Crawl Errors:
- If a page has a crawl error, it means Googlebot had trouble accessing or reading the page.
- Fix: Ensure there are no server issues, the page URL is correct, and there are no issues with redirects or 404 errors.
- Blocked by Robots.txt:
- If your robots.txt file blocks access to important pages, Google won’t be able to index them.
- Fix: Check your robots.txt file to ensure you are not blocking essential pages by mistake. Use GSC’s robots.txt Tester to validate the file.
- Noindex Tag:
- Pages may have a noindex directive in their HTML code, preventing them from being indexed.
- Fix: Ensure that the pages you want indexed do not contain a noindex meta tag in their HTML source code.
- Canonicalization Issues:
- Sometimes, Google might index the wrong version of a page, especially in the case of duplicate content.
- Fix: Check that you’ve properly implemented canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page. Use the URL Inspection Tool to see which page Google is treating as the canonical.
2. Fixing Common Errors in Google Search Console
Several errors might appear in the Coverage Report that require fixing to ensure proper indexing. These errors can significantly affect your site’s SEO performance.
Common Errors and Fixes:
- 404 Errors (Page Not Found):
- A 404 error means that a page is missing or unreachable.
- Fix: Check the page URL and ensure it exists. If the page is intentionally removed, set up a proper 301 redirect to another relevant page to avoid broken links.
- 500 Errors (Server Errors):
- 500 errors indicate a server issue, preventing Googlebot from crawling your pages.
- Fix: Contact your hosting provider to resolve server issues or check if server configurations are causing downtime.
- Soft 404 Errors:
- These occur when a page appears to be returning a 200 OK status but is actually empty or irrelevant (like a “not found” page).
- Fix: Ensure that you’re returning the correct status codes for pages that don’t exist (404 or 410), and avoid showing an empty page with a 200 OK status.
- Redirect Errors:
- Incorrect or excessive redirects can cause indexing issues, especially if there are redirect loops or chains.
- Fix: Ensure that all redirects are clean and lead to the right destination page, with no unnecessary loops or chains.
3. Ensuring All Pages Are Properly Indexed
To make sure that your pages are indexed properly, follow these best practices:
1. Check URL Coverage in GSC Regularly
Always monitor your site’s Coverage report in GSC. If certain pages are not indexed, check for errors or exclusions. If pages are incorrectly excluded (e.g., marked as noindex or blocked), address those issues promptly.
2. Use the URL Inspection Tool
Use the URL Inspection Tool to test individual pages and confirm their indexing status. This tool will tell you if Google has indexed the page and if there are any issues with crawling or indexing.
3. Review Internal Linking
Make sure that pages you want indexed are properly linked internally from other parts of your website. Internal links help Googlebot discover and crawl your pages more easily. If pages aren’t linked internally, Google may overlook them.
4. Submit Sitemaps
A sitemap is a vital tool for helping search engines crawl and index your site’s pages. Make sure your sitemap is up to date and contains all important pages.
- In GSC, go to Sitemaps and submit your sitemap if it isn’t already there. This will help ensure that all pages are found and crawled by Googlebot.
5. Fixing Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and lead to improper indexing. Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of the page, and ensure your content is original and high-quality.
4. Monitor Indexing with GSC Alerts
Google Search Console allows you to set up alerts for various issues. These alerts can notify you when indexing issues or other problems occur, so you can fix them before they cause long-term damage to your SEO efforts.
To set up alerts:
- Go to Settings in GSC.
- Select Change of Address or Email Notifications to receive alerts about new issues or problems affecting your site’s performance.
aIn this tutorial, we’ve explored how to use Google Search Console (GSC) to improve your website’s SEO and scale your traffic effectively. Here are the key takeaways:
- GSC Overview: Google Search Console provides valuable insights into your website’s performance, including data on clicks, impressions, and indexing issues.
- Keyword Research: By analyzing GSC’s search query data, you can identify high-traffic keywords, discover new ranking opportunities, and use this information to optimize your content for organic reach.
- On-Page SEO Optimization: GSC allows you to track and improve your content by incorporating relevant keywords, fixing indexing problems, and ensuring your pages are crawlable.
- Technical SEO Troubleshooting: Use GSC’s tools to identify and fix common technical issues, such as 404 errors, crawl issues, and redirect problems, which can directly impact your site’s search engine ranking.
- Advanced Insights and Troubleshooting: For advanced users, exporting GSC data to spreadsheets and using filters and regular expressions will help uncover deeper insights and fine-tune your SEO strategy.
- Indexing and Coverage Reports: Regularly check the Coverage Report and URL Inspection Tool to ensure all pages are indexed and free of errors that could hinder your rankings.
Action Steps
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of how to use Google Search Console, it’s time to put these strategies into action:
- Review Your GSC Data Regularly: Regularly monitor your performance, indexing status, and search queries to identify areas for improvement.
- Optimize Content with Identified Keywords: Use keyword insights from GSC to optimize your pages for higher search rankings.
- Fix Indexing Issues: Act quickly to resolve any indexing problems and ensure all your important pages are included in Google’s index.
- Implement Technical SEO Fixes: Address crawl errors, 404s, and redirect issues to make your site more search engine-friendly.
By implementing these GSC strategies, you’ll be able to enhance your website’s visibility, improve search rankings, and drive more organic traffic. Take action today and start making the most of Google Search Console to propel your SEO efforts forward!




